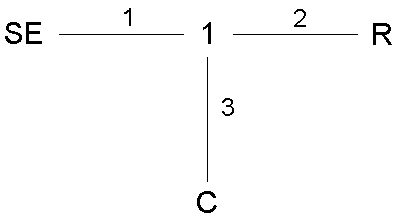
Bondgraph Analysis Program Synthesis
BAPS is a program system for presenting and analysing bondgraphs.
BAPS analyses linear and nonlinear bondgraphs and assigns causalities.
BAPS converts a BAPS-program into a simulation model, e.g. for SIMUL_R.
BAPSDRAW allows for the graphical creation of BAPS-programs.
The BAPS-language
describes the bondgraph in bond-notation in a textual way.
- Element-constants can be formulated as constants or nonlinearities,
- the constituting nonlinear equations of elements can be specified directly,
- using logical switches time variant value and topological changes (in the bond connections) can be described,
- additionally unsteady state changes can be specified and
- table functions can be used.
Modern modelling methods
BAPS support the bondgraph-modelling by
- possibilities for partitioning in connected and disconnected partial graphs
- rapid prototyping in partial models,
- meta commands, like macros and text loops,
- language elements for using parallel computing simulation systems
- inclusion of partial differential equations (simulated using SIMUL_R™).
The BAPS-compiler
- performs causality checks and -assignments,
- checks linear and nonlinear systems for algebraic loops and
- creates optimized simulation models.
Simple example: RC-swinger/spring-damping system
Bondgraph:
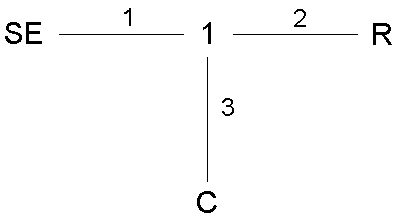
BAPS-model:
RC_System:
SE 1; 1 1 2 3; R 2; C 3;
{
CONSTANT tend=0.05, frequ=50, f=frequ*2*3.14, ampl=220;
EXTERN sin(1);
"termination condition"
TERMINATE t>=tend;
"element constants"
SE 1: SE1=ampl*sin(t*f);
R 2: R2=100;
C 3: C3=0.0001; q03=0; "initial charge"
}
BAPS is available on Windows- and Unix-plattforms for the simulation languages SIMUL_R™, ACSL™, Matlab™, Simulink™, Hybsys.
Use the info-form to request further information.
| Home |
Copyright Simutech 2002
Mail to webmaster |